Global Positioning System (GPS) is a United States satellite-based radio navigational, positioning, and time transfer system operated by the Department of Defense (DoD). The system provides highly accurate position and velocity information and precise time on a continuous global basis to an unlimited number of properly-equipped users. The system is extremely versatile in its uses and can be found in all sorts of environments from military to civilian aviation and beyond.
Three segments constitute the GPS system: space segment, control segment, and user segment.
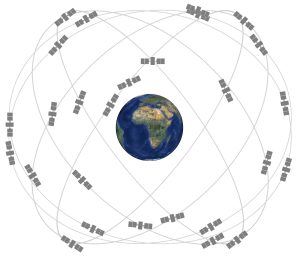
Presently, the space segment is made up of 35 satellites orbiting 11,000 miles above earth. This number however is not all that important and changes continuously as new satellites are launched into orbit. What is important is that the GPS constellation of satellites is designed so a minimum of five are always observable by a user anywhere on earth.
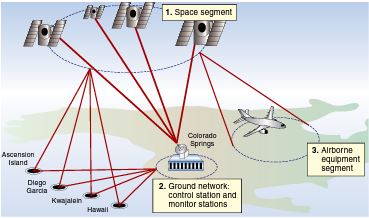
The control segment is a series of ground-based monitoring stations spread out at various locations around the world, all reporting back to a master control station in Colorado Springs, CO. These stations along with antennas and up-links are able to monitor the health, orbital state, and navigational message of each passing satellite.
Lastly we have the user segment which is essentially the GPS receiver. To obtain an accurate fix the GPS receiver uses data from a minimum of four satellites to yield a three dimensional position (latitude, longitude, altitude) and time solution. GPS-capable aircraft must be equipped with a GPS receiver. The receiver is not only capable of determining your position but even more importantly verifying the integrity of the signal. This is referred to as receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) and will determine if the satellites are providing corrupted information. However not all GPS receivers have RAIM alerting capabilities; you should understand the limitations of the receiver in which you are using. A minimum of five satellites are required to perform RAIM with few exceptions. An accurate GPS position cannot be assured when RAIM capabilities are not available and thus GPS should not be relied upon. In all instances you should back up GPS with other forms of navigational aids or pilotage.
A few things to take away from this talk on GPS:
- A minimum of 5 satellites are observable by a user anywhere on earth.
- Four satellites are required to obtain an accurate fix.
- A minimum of 5 satellites are required to compute RAIM.
- Understand the limitations of the GPS receiver in which you are using.
For additional information you can check out www.gps.gov.
List of current GPS satellites in orbit ftp://tycho.usno.navy.mil/pub/gps/gpstd.txt




