In many instances, a pilot is required to have contact with ATC. But even when not required, a pilot finds it helpful to request their services. Today, we’re taking a look at radar assistance with words and pictures from the Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge.
Primary Radar
Radar is a device which provides information on range, azimuth, and/or elevation of objects in the path of the transmitted pulses. It measures the time interval between transmission and reception of radio pulses and correlates the angular orientation of the radiated antenna beam or beams in azimuth and/or elevation. Range is determined by measuring the time it takes for the radio wave to go out to the object and then return to the receiving antenna. The direction of a detected object from a radar site is determined by the position of the rotating antenna when the reflected portion of the radio wave is received.
Modern radar is very reliable and there are seldom outages. This is due to reliable maintenance and improved equipment. There are, however, some limitations which may affect ATC services and prevent a controller from issuing advisories concerning aircraft which are not under his or her control and cannot be seen on radar.
The characteristics of radio waves are such that they normally travel in a continuous straight line unless they are “bent” by atmospheric phenomena such as temperature inversions, reflected or attenuated by dense objects such as heavy clouds and precipitation, or screened by high terrain features.
ATC Radar Beacon System (ATCRBS)
The ATC radar beacon system (ATCRBS) is often referred to as “secondary surveillance radar.” This system consists of three components and helps in alleviating some of the limitations associated with primary radar. The three components are an interrogator, transponder, and radarscope. The advantages of ATCRBS are the reinforcement of radar targets, rapid target identification, and a unique display of selected codes.
Transponder
The transponder is the airborne portion of the secondary surveillance radar system and a system with which a pilot should be familiar. The ATCRBS cannot display the secondary information unless an aircraft is equipped with a transponder.
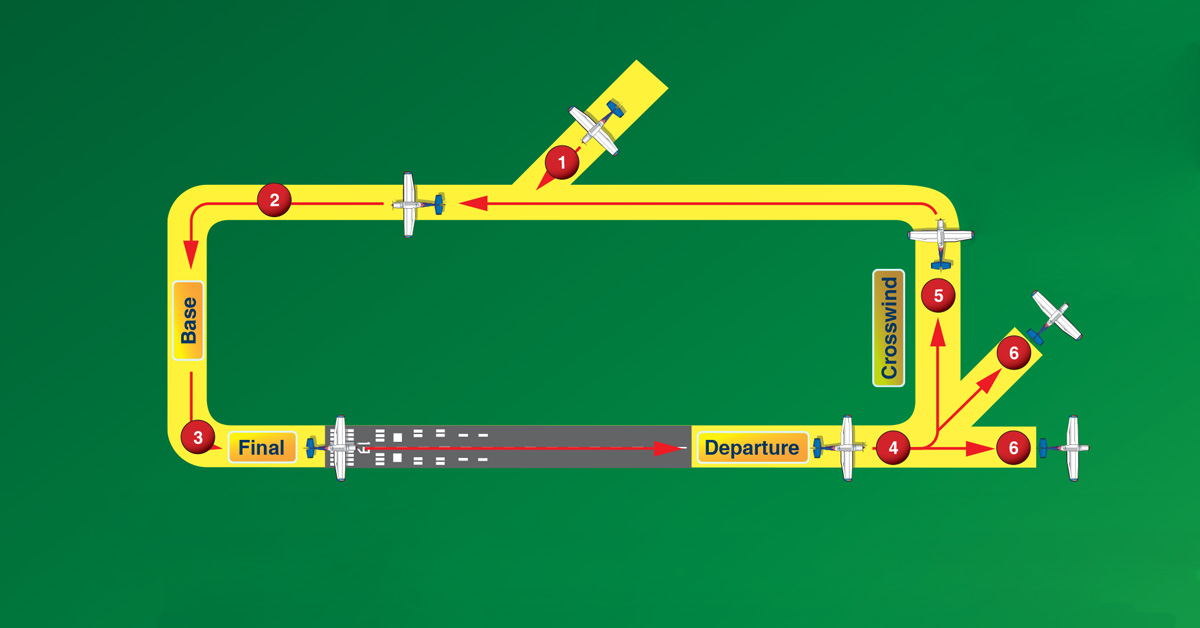
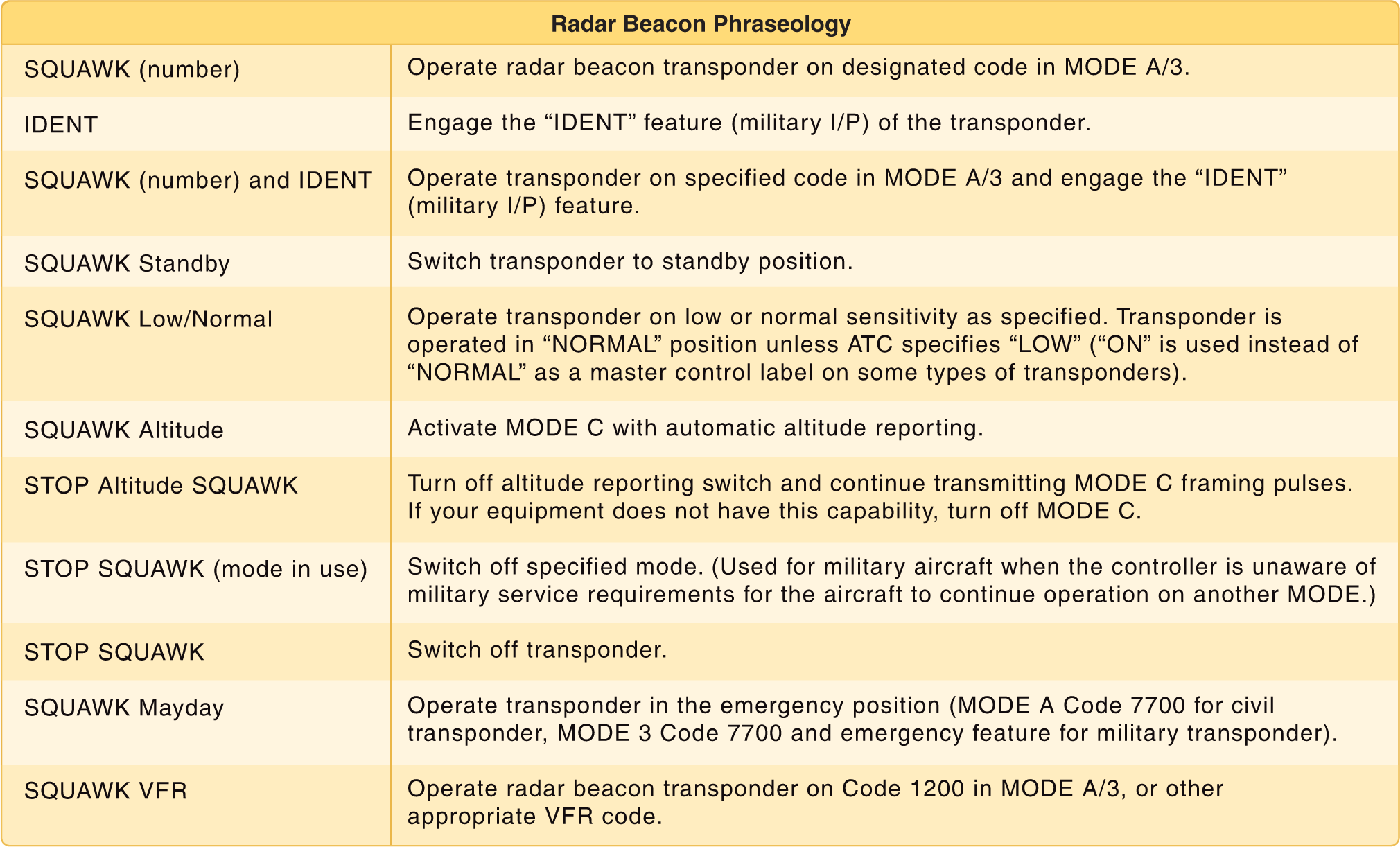
A transponder code consists of four numbers from 0 to 7 (4,096 possible codes). There are some standard codes, or ATC may issue a four-digit code to an aircraft. When a controller requests a code or function on the transponder, the word “squawk” may be used. Figure 1 lists some standard transponder phraseology. Additional information concerning transponder operation can be found in the AIM, chapter 4.
Radar Traffic Advisories
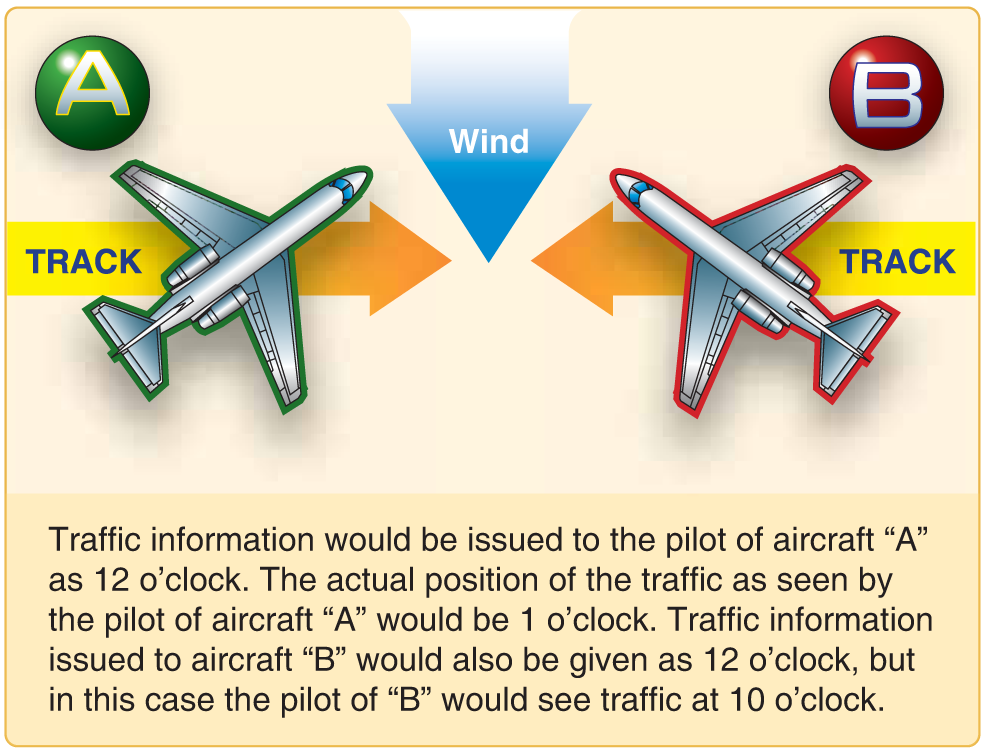
Radar equipped ATC facilities provide radar assistance to aircraft on instrument flight plans and VFR aircraft provided the aircraft can communicate with the facility and are within radar coverage. This basic service includes safety alerts, traffic advisories, limited vectoring when requested, and sequencing at locations where this procedure has been established. ATC issues traffic advisories based on observed radar targets. The traffic is referenced by azimuth from the aircraft in terms of the 12-hour clock. Also, distance in nautical miles, direction in which the target is moving, and type and altitude of the aircraft, if known, are given. An example would be: “Traffic 10 o’clock 5 miles east bound, Cessna 152, 3,000 feet.” The pilot should note that traffic position is based on the aircraft track, and that wind correction can affect the clock position at which a pilot locates traffic. This service is not intended to relieve the pilot of the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft. (Figure 2.)
In addition to basic radar service, terminal radar service area (TRSA) has been implemented at certain terminal locations. TRSAs are depicted on sectional aeronautical charts and listed in the A/FD. The purpose of this service is to provide separation between all participating VFR aircraft and all IFR aircraft operating within the TRSA. Class C service provides approved separation between IFR and VFR aircraft, and sequencing of VFR aircraft to the primary airport. Class B service provides approved separation of aircraft based on IFR, VFR, and/or weight, and sequencing of VFR arrivals to the primary airport(s).
We’ll be back on Thursday with a CFI report!