Today we will take Monday’s post on temperature inversions a step further with a discussion on atmospheric stability and the types of weather we can expect with a stable and unstable air mass.
Atmospheric stability is defined as the resistance of the atmosphere to vertical motion. A stable atmosphere resists an upward or downward movement. An unstable atmosphere allows an upward or downward disturbance to grow into a vertical (convective) current.
Determining the stability of the atmosphere requires measuring the difference between the actual existing (ambient) temperature lapse rate of a given parcel of air and the dry adiabatic rate (a constant 3°C per 1,000 feet lapse rate).
A stable layer of air would be associated with a temperature inversion. Warming from below, on the other hand, would decrease the stability of an air mass.
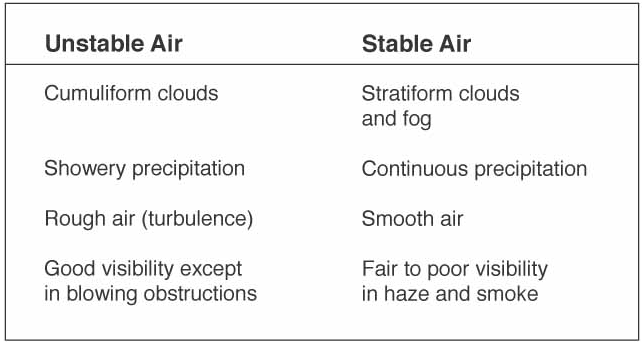
The conditions and characteristic of stable or unstable air masses are shown in the figure below.
Like most things in life their are benefits and drawbacks to both atmospheric conditions. While the visibility may be excellent in an unstable air mass you are likely to encounter turbulent conditions and possibly wind shear. In a stable air mass because the air is stagnant (or lack of vertical motion) you will have a much smoother ride however visibility could be decreased due to hazy conditions.
Take a look at some of these sample FAA knowledge test questions and see if you can answer them.
1. What type weather can one expect from moist, unstable air, and very warm surface temperatures?
A—Fog and low stratus clouds.
B—Continuous heavy precipitation.
C—Strong updrafts and cumulonimbus clouds.
2. What are the characteristics of stable air?
A—Good visibility; steady precipitation; stratus clouds.
B—Poor visibility; steady precipitation; stratus clouds.
C—Poor visibility; intermittent precipitation; cumulus clouds.
3. A moist, unstable air mass is characterized by
A—poor visibility and smooth air.
B—cumuliform clouds and showery precipitation.
C—stratiform clouds and continuous precipitation.
4. Which is a characteristic typical of a stable air mass?
A—Cumuliform clouds.
B—Showery precipitation.
C—Continuous precipitation.
Answers will be posted in the comments section.